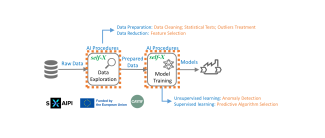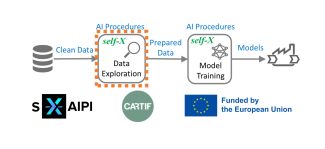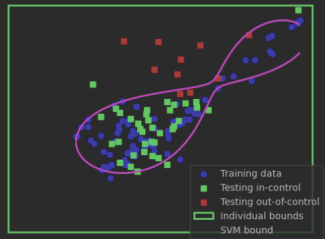
DIH4AI: I-PRAG-4 Demo for experiment - Process monitoring using one-class support vector machine
Jupyter notebook demonstrating usage of multivariate anomaly detection based on machine learning to process monitoring and detection of a suspicious state of a process.